来源:网络资源 2023-10-01 13:24:25
一般将来时
将来某个时间要发生的动作或存在的状态,也表示将来经常或重复发生的动作
一般将来时表示。
常与表示将来的时间状语连用,如:tomorrow,next year,soon等。
我们已经学习过一般现在时,它表示目前(现在)习惯或经常性的动作;以现在为基准,叙述过去某时的事情,用过去时;以现在为基准,叙述将来的事情,用将来时。
例1:I’m going to study tomorrow.我打算明天学习。
例2:I will/shall study tomorrow.我明天将要学习。
PART 01
一般将来时的构成
用助动词will/shall表示的一般将来时,本身没有人称和数的变化。
主语是第一人称(I或we)
在书面语中,时,常用助动词;
所有的人称
在口语中,都可以用。
如果在疑问句中,主语是第一人称(I或we)时,常用助动词shall。
一般将来时的肯定句
句型:主语+will/shall+动词原形+……
例1:Iwill/shallarrive in New York tomorrow morning.我明早到纽约。
例2:Wewillcome to see you next week.下周我们会来看你。
例3:Therewillbe a computer on every student’s desk in the future.将来,每位同学的桌子上都会有一台电脑。
一般将来时的否定句
句型:主语+will/shall+not+动词原形+……
例1:Iwill not/won’ttell him the matter.我不会把这件事告诉他的。
注:will not常用它的缩略式:won’t,读作[wəʊnt]。
例2:The teacherswon’twrite on the blackboard with chalk any more.老师们将不再用粉笔在黑板上写字。
一般将来时的疑问句
→ 句型:Will/Shall+主语+动词原形+……?
例1:—Willhe be back in two days?他两天后会回来吗?—Yes,hewill.是的,他会。/No,hewill not.不,他不会。
例2:—Shallwe have any class tomorrow?明天我们有课吗?—Yes,wewill/shall.是的,我们明天有课。/No,wewon’t/shall not.不,明天我们没课。
!
注意:
① Shall I/we...?常用来征求对方意见。
例:Shall I go home now?我现在可以回家了吗?
② Will you...? 问对方是否愿意或者表示客气的邀请或命令时
例:Will you please open the window?劳驾,您打开窗户好吗?
→ 句型:疑问词+will/shall+主语+动词原形+……?
例1:—When willMike arrive here tomorrow?迈克明天什么时候到这儿?
—He will arrive here at three o’clock.他明天3点钟到这儿。(简略回答:At three o’clock)
例2:—How manybookswillthey give us?他们会给我们多少本书呢?
—They will give us thirty books.他们会给我们30本书。(简略回答:Thirty books)
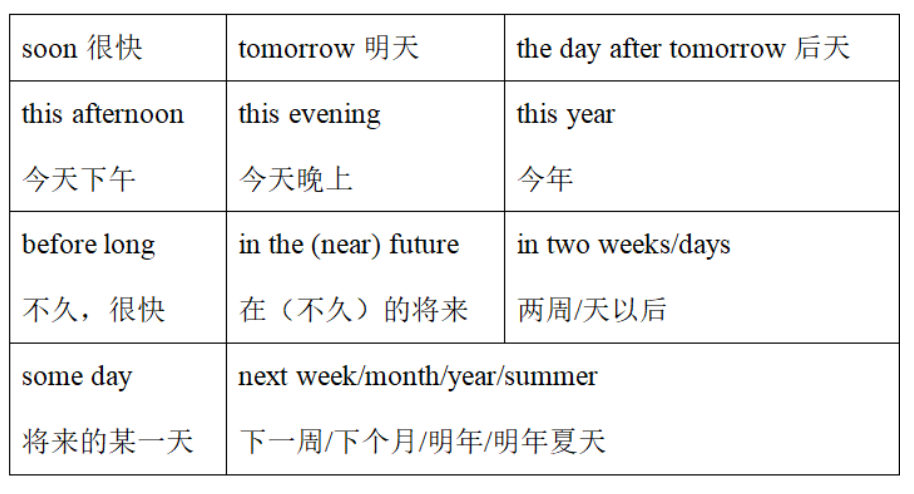
必背!!!和一般将来时连用的时间状语
PART 02
一般将来时的基本用法
表示将来的动作或状态
例1:My motherwillspend her holiday in Shanghai in August.8月份我妈妈将去上海度假。
例2:In the future,there’ll bea new school.将来这儿要建一所新学校。
用在一些主从复合句中
一般将来时在一些主从复合句的主句中表示将来的动作或状态。
例1:We’llhave a picnic if it doesn’t rain tomorrow.明天如果不下雨我们就去野餐。
Dickwillpass the exam if he studies harder.如果迪克再努力些,他就会及格。
PART 03
其他表示将来的结构
be going to+动词原形+……
对于将要发生的事情,或打算、计划、决定要做的事情,皆可以用“be going to+动词原形+……”句型来表示。
肯定句
句型:主语+be going to+动词原形+……
例1:Heis going totravel around the world.:他计划周游世界。
例2:They’re going tohave a picnic this weekend.他们这个周末要去野餐。
注意:be going to后面的动词一定要用原形。
否定句
句型:主语+be not going to+动词原形+……
例1:I’m not going tobe a teacher.我不打算当老师。
例2:We’re not going tohave any class next week.下周我们不上课。
注意:
此句型含有be动词,所以它的否定句与一般含有be动词的句型相同,只要在be动词后面加上not即可,其余保持不变。
一般疑问句
句型:Be+主语+going to+动词原形+……?
例:—Are you going tobe a doctor when you grow up?你长大了,打算当一名医生吗?
—Yes,I am.是的,我想。/No,I’m not.不,我不想。
注意:
此句型中有be动词,所以它的一般疑问句的构成法也和含有be动词的句型相同,只要把be动词放在句首,就使其成为一般疑问句。
特殊疑问句
句型:疑问词+be+主语+going to+动词原形+……?
Where
例1:is she going tohave her birthday party?她打算在哪儿举办生日聚会?
How
例2:are they going tospend their holidays?假期他们准备怎么过?
PART 04
be going to和will/shall的区别
对初中阶段来讲,“be going to+动词原形”和“will/shall+动词原形”一般可以互换使用。
但在现代英语中,特别是在口语中,表将来时多用“be going to+动词原形”这一形式。它们的主要区别在于:
be going to+动词原形
表示主观上打算、计划或意图
例:Heis going tochange his job.他打算换工作。
注意:换工作是事先考虑好的,所以用be going to
will/shall+动词原形
未经事先考虑的意图
例:There is somebody at the door.I’llgo and open it.(门口有人,我去开门。)
注意:I’ll go and open it.去开门显然是未经事先考虑的意图,在此,不宜说I’m going to open it.
编辑推荐:

欢迎使用手机、平板等移动设备访问中考网,2023中考一路陪伴同行!>>点击查看